Boas pessoal!
Para quem quiser importar os dados de consumo elétrico da E-Redes para o Home Assistant , sem necessidade de instalar dispositivos adicionais ligados à box/contador, podem seguir este método.
Passo 1 – Download dos dados
Acedam ao Balcão Digital da E-Redes e façam o download das estatísticas mensais de consumo :
 https://balcaodigital.e-redes.pt/login
https://balcaodigital.e-redes.pt/login
Passo 2 – Instalar a integração
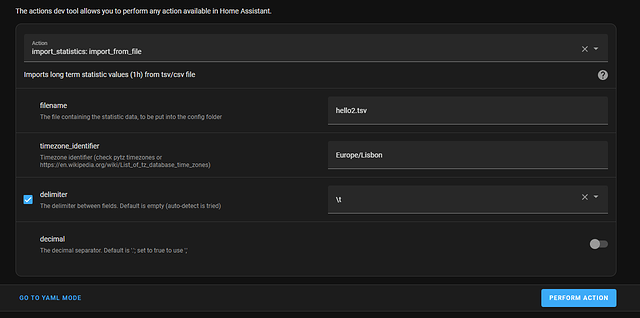
Instalem a integração Import statistics no Home Assistant:
 https://github.com/klausj1/homeassistant-statistics
https://github.com/klausj1/homeassistant-statistics
Passo 3 – Preparar o ficheiro para importação
Utilizem este pedaço de código em Python para criar o ficheiro no formato correto, que depois será importado através da ferramenta referida acima.
import sys
import math
import datetime
import pandas as pd
from datetime import timezone
# ---------------- CONFIG (from TemplateDataPrepare.py) ----------------
inputFileDateColumnName = "Data"
inputFileTimeColumnName = "Hora"
inputFileDateTimeColumnFormat = "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M"
inputFileNumHeaderRows = 8
inputFileExcelSheetName = 0
valueColumnName = "Consumo registado (kW)"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
def load_excel(file_path: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
print(f"Loading Excel file: {file_path}")
df = pd.read_excel(
file_path,
sheet_name=inputFileExcelSheetName,
skiprows=inputFileNumHeaderRows,
)
return df
def prepare_datetime(df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
df["_DateTime"] = pd.to_datetime(
df[inputFileDateColumnName].astype(str)
+ " "
+ df[inputFileTimeColumnName].astype(str),
format=inputFileDateTimeColumnFormat,
utc=True,
)
# Remove timezone
df["_DateTime"] = df["_DateTime"].dt.tz_localize(None)
# Sort
df.sort_values(by="_DateTime", inplace=True)
# Convert to UNIX timestamp
df["_Timestamp"] = (df["_DateTime"].astype("int64") / 1_000_000_000).astype("int64")
return df
def recalculate_energy(df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
previous_index = None
for index in df.index:
value = df.at[index, valueColumnName]
if math.isnan(value):
value = 0.0
# Convert kW 15-min interval → kWh
value = value / 4
if previous_index is not None:
value += df.at[previous_index, valueColumnName]
df.at[index, valueColumnName] = round(value, 3)
previous_index = index
return df
def extract_month_year(df: pd.DataFrame):
first_date = df["_DateTime"].iloc[0]
return f"{first_date.month:02d}", f"{first_date.year}"
def generate_homeassistant_tsv(
df: pd.DataFrame,
previous_total: float,
output_file: str,
):
print(f"Creating Home Assistant file: {output_file}")
with open(output_file, "w") as f:
f.write("statistic_id\tunit\tstart\tstate\tsum\n")
for _, row in df.iterrows():
dt_obj = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(
row["_Timestamp"], tz=timezone.utc
)
# Keep only full hours
if dt_obj.minute != 0:
continue
dt_str = dt_obj.strftime("%d.%m.%Y %H:%M")
value = row[valueColumnName] + previous_total
value = f"{value:.3f}"
f.write(
f"sensor:not_existing_total_energy_consumption\t"
f"kWh\t{dt_str}\t{value}\t{value}\n"
)
def main():
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print("Usage:")
print(" python eredes_to_homeassistant.py <xlsx_file> <previous_month_total>")
sys.exit(1)
xlsx_file = sys.argv[1]
previous_total = float(sys.argv[2])
df = load_excel(xlsx_file)
df = prepare_datetime(df)
df = recalculate_energy(df)
month, year = extract_month_year(df)
output_file = f"{month}_{year}.tsv"
generate_homeassistant_tsv(df, previous_total, output_file)
print("Done ✔")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Antes de executar o script
Antes de correr o script, certifiquem-se de que têm todas as bibliotecas Python necessárias instaladas.
Utilização
1 - python eredes_to_homeassistant.py <ficheiro_xlsx> <total_do_mes_anterior>
2 -
Espero que isto seja útil para alguém!